

NTSE SAT Mathematics - Co Ordinate Geometry
Exam Duration: 45 Mins Total Questions : 30
Find the coordinates of a point A, where AB is the diameter of a circle whose centre is (2, -3) and Bis (1,4)
- (a)
(3,-10)
- (b)
(3,10)
- (c)
(-3,10)
- (d)
none of these
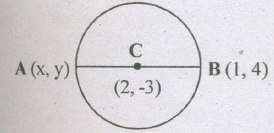
LetC be the centre of the circle, then C= (2,-3)
Let the coordinates of the point A be (x, y)
∴ AB is a diameter of a circle whose centre is C
∴ C is the mid-point of AB.
∴ \((\frac{x+1}{2},\frac{y+4}{2})=(2,-3)\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{x+1}{2}=2 \Rightarrow x+1=4 \Rightarrow x=3\)
Similarly \(\frac{y+4}{2}=-3 \Rightarrow y+4=-6 \Rightarrow y=-2\)
A=(3,-10)
If (1, 2) (4, y) (x, 6) and (3, 5) are the vertices of a parallelogram taken in order, find x and y.
- (a)
(2,3)
- (b)
(6,3)
- (c)
(-2,3)
- (d)
(-6,-3)
Let A(l, 2), B(4, V), C(x, 6) and D(3, 5)
We know, diagonals of parallelogram bisect each other, so, coordinates of mid-point of diagonal AC= Co-ordinates of mid-point of diagonal BD \(\Rightarrow (\frac{1+x}{2},\frac{2+6}{2})=(\frac{4+3}{2},\frac{y+5}{2})\)
\(\Rightarrow (\frac{1+x}{2},4)=(\frac{7}{2},\frac{y+5}{2})\)
\(\Rightarrow \frac{1+x}{2}=\frac{7}{2}\Rightarrow 1+x=7 \Rightarrow x=6 and \)
y+5=8 ⇒ y=3
Find the area of a rhombus if its vertices are (3, 0) (4, 5) (-1,4) and (:-2, -1) taken in order.
- (a)
34 sq units
- (b)
24 sq units
- (c)
20 sq units
- (d)
44 sq units
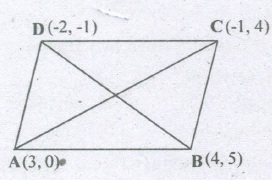
We know,
Area of a rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\)[product of its diagonals]
∴ Area of the rhombus ABCD =\(\frac{1}{2}\)(ACxBD)
\(=\frac{1}{2}[ (\sqrt{(-1-3)^{2}+{(4-0)^{2}}})+(\sqrt{(-2-4)^{2}{(-1-5)^{2}}})]\)
\(=\frac{1}{2}[(\sqrt{16+16})(\sqrt{36+36})]\)
\(=\frac{1}{2}(\sqrt{32})(\sqrt{72})=\frac{1}{2}(4\sqrt{2})(6\sqrt{2})\)
=24 square units
Find the value of p for which th~ points (-1, 3) (2, p) and (5, -1) are collinear
- (a)
2
- (b)
3
- (c)
1
- (d)
4
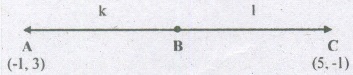
If the points A. Band C are collinear, then let B divide AC in the ratio k: 1 internally.
\(B=[\frac{(k)(5)+(1)(-1)}{k+1},\frac{(k)(-1)+(1)(3)}{k+1}]\)
\(B=[\frac{5k-1}{k+1},\frac{-k+3}{k+1}]\)
But B is (2, p)
\(\therefore \frac{5k-1}{k+1}=2 \Rightarrow 5k-1=2(k+1)\)
\(\Rightarrow 5k-2k=3\)
3k=3 ⇒ k=1
and \(\frac{-k+3}{k+1}=p \Rightarrow \frac{-1+3}{1+1}=p\)
⇒ p=1
Three consecutive vertices of a paralleloqram are (-2, 1) (1, 0) and (4, 3). Find the fourth vertex.
- (a)
(1,4)
- (b)
(1, -2)
- (c)
(-1, 2)
- (d)
(-1, -2)
Let the fourth vertex be (x, y)then
\(\frac{x+1}{2}=\frac{-2+4}{2} \Rightarrow x=1\)
\(\frac{y+0}{2}=\frac{1+3}{2}\Rightarrow y=4\)
[ .'. Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other]
Which of the following points be collinear with (6, 9) (0,1)
- (a)
(6, -7)
- (b)
(-6, 7)
- (c)
(-6, -7)
- (d)
none of these
Checking from the options, we find point (-6, -7) collinear with two points (6, 9) (0, 1).
The triangle formed by joining the vertices (2, -2) (-2, 1) and (5, 2) will be a
- (a)
Acute triangle
- (b)
Obtuse triangle
- (c)
Right-angled triangle
- (d)
None of these
A = (2, -2), B = (-2, 1) and C = (5, 2)
AB2= (_2_2)2+ (1+2)2= 16+9=25
BC2=(5+2)2+(2-1)2=49+1 =50
AC2=(5-2)2+(2+2)2=9+16=25
AB2+AC2=BC2= >△ ABCis a right angled triangle.
In the adjoining figure, P and Q have co-ordinates (4,6) and (0; 3) respectively. Find the co-ordinates of Rand area of quadrilateral OAPQ.
- (a)
(-4,0) and 18 sq units
- (b)
(4, 0) and 18 sq units
- (c)
(0, 4) and 15 sq units
- (d)
None of these
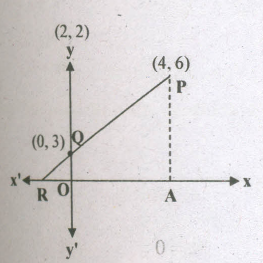
Let OR = x units
i) △ QOR ~ △ PAR
⇒ \(\frac{PA}{AR}=\frac{QO}{OR}⇒\frac{6}{x+4}=\frac{3}{x}\)
⇒ \(\frac{x}{x+4}=\frac{3}{6}\Rightarrow \frac{x}{x+4}=\frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow x=4\)
:. The co-ordinates of Rare (-4, 0)
ii) Quadrilateral of OAPQ is a trapezium
∴ Area of trapezium OAPQ
=\(\frac{1}{2}(OQ+AP)\times OA\)
=\(\frac{1}{2}(3+6)\times4\)
=\(\frac{1}{2}\times9\times4=18\) sq units.
A(3, 2) and B(-2, 1) are two vertices of a triangle ABC, whose centroid G has a co-ordinate \((\frac{5}{3},\frac{1}{3})\) .Find the coordinates of the third vertex C of the triangle.
- (a)
(-4,4)
- (b)
(-4,-4)
- (c)
(4,-4)
- (d)
none
A(3, 2) B(-2, 1)
Let the coordinates of the third vertex C of the triangle be (x, y)
Then
\(G(\frac{(3)+(-2)+(x)}{3},\frac{(2)+(1)+(y)}{3})\)
\(⇒ G(\frac{x+1}{3},\frac{y+3}{3})\)
But G is \((\frac{5}{3},\frac{-1}{3})\) (Given)
∴ \(\frac{x+1}{3} =\frac{5}{3}⇒x=4\)
\(\frac{y+3}{3}=\frac{-1}{3}⇒y=-4 \)
∴ C=(4,-4)
The mid-point of the diagonal BD of a rhombus is (3, 4).lfthe coordinate of point B(1, 5) the coordinate of point D will be
- (a)
(3,5)
- (b)
(5,3)
- (c)
(3, 1)
- (d)
(5, 1)
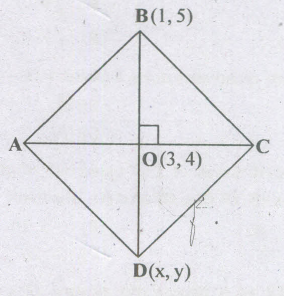
Let, D=(x, y)
We know, 0 is the midpoint of diagonal BD
So, (3,4)=\((\frac{1+x}{2},\frac{5+y}{2})\)
\(⇒ \frac{1+x}{2}=3\) and \(\frac{5+y}{2}=4\)
⇒ x=5 , y=3
D=(5,3)
In which quadrant does a point (-3, -3) lie?
- (a)
I
- (b)
II
- (c)
III
- (d)
IV
The coordinates of the centroid of the triangle with vertices (0, 0) (3a, 0) and (0, 3b) are
- (a)
(-a, -b)
- (b)
(-a, b)
- (c)
(a, -b)
- (d)
(a, b)
\(x=\frac{0+3a+0}{3}=a\)
\(y=\frac{0+0+3b}{3}=b\)
If OPQR is a rectangle where 0 is the origin and P{3, 0) and R(O, 4) then the coordinates of Q are
- (a)
(3, -4)
- (b)
(3, 4)
- (c)
(4, 3)
- (d)
(-3, -4)
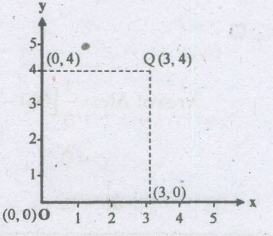
=(3,4)
=Q
The coordinates of the point of intersection x-axis and y-axis are:
- (a)
(0, 0)
- (b)
(0,1)
- (c)
(1,0)
- (d)
(1,1)
Point of intersection is 0, the origin
The point equidistant from the points (0, 0) (2, 0) and (0,2) is
- (a)
(1,2)
- (b)
(2,1)
- (c)
(2, 2)
- (d)
(1,1)
The coordinates of the point, dividing the join of the points (5, 0) and (0,4) in the ratio 2:3 internally are
- (a)
\((3,\frac{8}{5})\)
- (b)
\((1,\frac{4}{5})\)
- (c)
\((\frac{5}{2},\frac{3}{4})\)
- (d)
\((2,\frac{12}{5})\)
\(x=\frac{2(0)+3(5)}{2+3}=3\)
\(y=\frac{2(4)+3(0)}{2+3}=\frac{8}{5}\)
If the points (0, 0), (a, 0) and (0, b) are collinear
- (a)
a=b
- (b)
a+b=0
- (c)
ab=0
- (d)
a≠b
Area of △le= \(\frac{1}{2}\)[0(0 -b) +a(b -0) +0(0-0)]
=0
⇒ ab=0
What is the area of the triangle formed by the point (0, 0) (3, 0) and (0, 4)
- (a)
6
- (b)
12
- (c)
3
- (d)
24
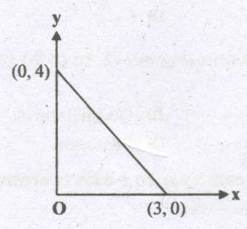
Area = \(\frac{3\times4}{2}=6\)
Find the coordinates of the centroid of a !J.ABC with vertices A(x1 ,y1), B(x2 ,y2), C(x3 ,y3)
- (a)
\((\frac{x_1+x_2}{3},\frac{y_1+y_2}{3})\)
- (b)
\((-\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3},\frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3})\)
- (c)
\((\frac{x_1+x_2,x_3}{3},\frac{y_1+y_2,y_3}{3})\)
- (d)
None of these
We know, centroid of a △le divides each median of the triangle from the vertex in the ratio 2:1
Let D be the midpoint of BC.
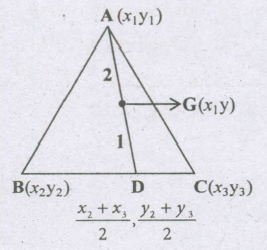
Let G(x, y) be centroid of △ABC
Then, G will divide AB internally in the ratio 2:
\(\therefore x=\frac{2(\frac{x_2+x_3}{2})+1(x_1)}{2+1}=\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3}\)
\(y=\frac{2(\frac{y_2+y_3}{2})+1(y_1)}{2+1}=\frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3}\)
Hence, the coordinates of the centroid are given by
\((\frac{x_1+x_2+x_3}{3}.\frac{y_1+y_2+y_3}{3})\)
Find the point on the x-axis which is equidistant from (2, -5) and (-2, 9)
- (a)
(7,0)
- (b)
(0,7)
- (c)
(0, -7)
- (d)
(-7,0)
We know, point on the x-axis is of the form (x, 0) So, let the point P(x, 0) be equidistant from A(2, -5) and B(-2, 9). Then
PA=PB
⇒ PA2=PB2
⇒(2-x)2+(-5-0)2=(-2-x)3+(9-0)2
⇒4+x2-4x+25=4+x2+4x+81
⇒ 8x=-56
⇒ x=-7
Hence, required-point is (-7, 0)
The quadrilateral formed by joining the points (4, 5), (7,6), (4, 3), (1, 2)
- (a)
Rectangle
- (b)
Rhombus
- (c)
Pallelogram
- (d)
Square
A(4, 5) B(7, 6) C(4, 3) D(1, 2)
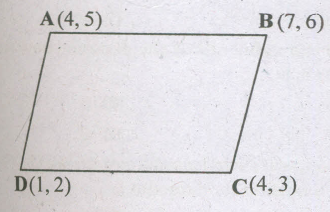
\(AB=\sqrt{(7-4)^{2}+{(6-5)^{2}}}=\sqrt{9+1}=\sqrt{10}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{(4-7)^{2}+{(3-6)^{2}}}=\sqrt{18}=3\sqrt{2}\)
\(CD=\sqrt{(1-4)^{2}+{(2-3)^{2}}}=\sqrt{9+1}=\sqrt{10}\)
\(DA=\sqrt{(4-1)^{2}+{(5-2)^{2}}}=\sqrt{18}=3\sqrt{2}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{(4-4)^{2}+{(3-5)^{2}}}=2\)
\(BD=\sqrt{(1-7)^{2}+{(2-6)^{2}}}=\sqrt{52}\)
We see, AB=CD, BC=DA and AC≠BD (opposite sides are equal but diagonals are unequal)
Hence, quadrilateral ABCDis a parallelogram
Find the coordinates of the point which divides the join of (-1,7) and (4, -3) in the ratio 2:3
- (a)
(-1, 3)
- (b)
(-1, -3)
- (c)
(1, -3)
- (d)
(1, 3)
Let the coordinates of the required point be (x, y)
Then, \(x=\frac{m_1x_1+m_2x_1}{m_1+m_2}\)
\(=\frac{(2)(4)+(3)(-1)}{2+3}=\frac{5}{5}=1\)
\(y=\frac{m_1y_2+m_2y_1}{m_1+m_2}\)
\(=\frac{(2)(-3)+(3)(7)}{2+3}=3\)
Hence, the required point (1, 3)
If the points (1, 2) (-1, x) and (2, 3) are collinear, then the value of x is
- (a)
2
- (b)
0
- (c)
-1
- (d)
1
1(x-3)-1(3-2)+2(2-x)=0
⇒ x-3-3+2+4-2x=0
x=0
The triangles with vertices (-2, 1)(2, -2) and (5, 2) is
- (a)
Scalene
- (b)
Equilateral
- (c)
Isosceles
- (d)
Right angled isosceles
\(AB=\sqrt{(2+2)^{2}+(-2-1)^{2}}=5\)
\(BC=\sqrt{(5-2)^{2}+(2+2)^{2}}=5\)
\(CA=\sqrt{(-2-5)^{2}+(1-2)^{2}}=\sqrt{50}\)
∴ AB=BC
AB2+BC2=25+25=50 = CA2
ஃ right angled isoseles
Find the value of k if the distance between (k, 3) and (2,3) is 5
- (a)
5
- (b)
6
- (c)
7
- (d)
8
\(\sqrt{(R-2)^{2}+(3-3)^{2}}=5\)
⇒ R-2=5
⇒ R=7
The opposite vertices of a square are (5, -4) and (-3, 2). The length of its diagonal is
- (a)
6
- (b)
8
- (c)
10
- (d)
12
Length=\(\sqrt{(-3-5)^{2}+(2+4)^{2}}=10\)
The vertices of a triangle are (3, 5) (5, 7) and (-5, 9) Find the x-coordinate of the centroid of the triangle
- (a)
0
- (b)
1
- (c)
2
- (d)
3
x=\(\frac{3+5+(-5)}{3}=1\)
The coordinates of the mid-point of the line-segment joining the points (x1 ,y1) and (x2,y2) are
- (a)
\((x_1+x_2,y_1+y_2)\)
- (b)
\((\frac{x_1+x_2}{2},\frac{y_1+y_2}{2})\)
- (c)
\((\frac{x_1+x_2}{4},\frac{y_1+y_2}{4})\)
- (d)
(x1x2,y1y2)
Mid point formula
Theclosedfigure with vertices (-2, 0) (2, 0) (2, 2) (O, 4) and(-2, 2) is a
- (a)
Triangle
- (b)
Quadrilateral
- (c)
Hexagon
- (d)
Pentagon
Number of points (vertices) = 5
∴ Pentagon.
Which of the following is the co-ordinate of point that divides the line PQ with P{-1, 2) and Q{-2, -1) externally in the ratio 3:2 ?
- (a)
(4,7)
- (b)
(4,-7)
- (c)
(-4,-7)
- (d)
(-4,7)
The required coordinate is
\((\frac{-3\times2-1(-1)\times2}{3-2},\frac{3(-1)-2(2)}{3-2})=(-4,-7)\)







