

SAT Mathematics - Quadrilaterals
Exam Duration: 45 Mins Total Questions : 30
The length of the diagonal BD of the parallelogram ABCD is 18 cm. If P and Q are the Centroid of the \(\Delta \)ABC and \(\Delta \)ADC repectively then the length of the line segment PQ is
- (a)
4 cm
- (b)
6cm
- (c)
9 cm
- (d)
12 cm
ABCD is a cyclic trapezium whose sides AD and BC are parallel to each other. If =72\(\circ\) then the measure of the
=72\(\circ\) then the measure of the .jpg) is
is
- (a)
162\(\circ\)
- (b)
18\(\circ\)
- (c)
108\(\circ\)
- (d)
72\(\circ\)
In a quadrilateral ABCD, with unequal sides, if the diagonals AC and BD intersect at right angles then
- (a)
AB2+BC2=CD2+DA2
- (b)
AB2+CD2=BC2+DA2
- (c)
AB2+AD2=BC2+CD2
- (d)
AB2+BC2=2(CD2+DA2)
Measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon can never be
- (a)
105o
- (b)
150o
- (c)
108o
- (d)
110o
A parallelogram ABCD has sides AB=24 cm; AD= 16cm. The distance between the sides AB and DC is 10cm. Find the distance between the sides AD and BC.
- (a)
16 cm
- (b)
18 cm
- (c)
15 cm
- (d)
26 cm
A square is of area 200 sq.m. Anew square is formed such a way that the length of its diagonal is \(\sqrt 2\) times of the diagonal of the given square. Then the area of the new square formed is
- (a)
200\(\sqrt 2\) sq.m
- (b)
400\(\sqrt 2\) sq.m
- (c)
400 sq.m
- (d)
800 sq.m
If a square and a rhombus stand on the same base, then the ratio of the areas of the square and the rhombus is
- (a)
equal to \(\frac1 4\)
- (b)
equal to \(\frac1 2\)
- (c)
equal to 1
- (d)
greater than 1
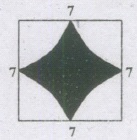
The area of the shaded region is
- (a)
49\(\left( 1-\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \right) \)
- (b)
49\(\left( \frac { \pi -1}{ 4 } \right) \)
- (c)
49\((1-\pi)\)
- (d)
none of these
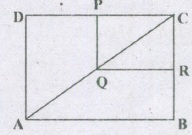
In the figure, ABCD and PQRS are rectangles, where Q is the mid-point of AC then
- (a)
DP=PC
- (b)
\(\frac1 3\)PR=\(\frac3 2\)DB
- (c)
DP=PQ
- (d)
DP=\(\frac1 2\)AC
A diagonal of a quadrilateral is a line segment that joins two-----vertices of the quadrilateral
- (a)
equal
- (b)
unequal
- (c)
opposite
- (d)
none of these
The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is-----right angles
- (a)
three
- (b)
four
- (c)
five
- (d)
none of these
A quadrilateral is convex if for each side, the remaining-----lie on the same side of the line containing the side
- (a)
Vertices
- (b)
opposite
- (c)
points
- (d)
none of these
The measure of each angle of a convex 'quadrilateral is-----180\(\circ\)
- (a)
more than
- (b)
less than
- (c)
more or less than
- (d)
none of these
In parallelogram, two adjacent angles are
- (a)
complementary
- (b)
supplementary
- (c)
acute
- (d)
none of these
Two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are equal. What is the measure of each?
- (a)
180\(\circ\)
- (b)
360\(\circ\)
- (c)
90\(\circ\)
- (d)
none of these
Two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are as 2:3. Find the measure of all the angles
- (a)
72\(\circ\), 108\(\circ\), 72\(\circ\), 108\(\circ\)
- (b)
62\(\circ\), 108\(\circ\), 62\(\circ\), 108\(\circ\)
- (c)
108\(\circ\), 108\(\circ\), 62\(\circ\), 62\(\circ\)
- (d)
none of these
A regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle with centre O. Then, the angle subtended by each side of the square of the centre O is
- (a)
80\(\circ\)
- (b)
90\(\circ\)
- (c)
60\(\circ\)
- (d)
45\(\circ\)
The ratio of the area of a square to that of the square drawn on its diagonals is
- (a)
1:1
- (b)
1:2
- (c)
1:3
- (d)
1:4
If ABCD is a parallelogram with two adjacent angles A and B equal to each other, then the parallelogram is a
- (a)
square
- (b)
rhombus
- (c)
rectangle
- (d)
both A or C
The length of the diagonals of a rhombus are 16 cm and 12cm. The side of the rhombus is
- (a)
12
- (b)
13
- (c)
14
- (d)
15
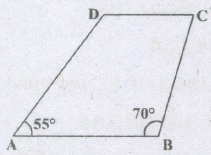
In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium in which AB||DC. If \(\lfloor A\)=55\(\circ\) and \(\lfloor B\)=70\(\circ\), then \(\lfloor C\) and \(\lfloor D\) are respectively
- (a)
140\(\circ\), 125\(\circ\)
- (b)
100\(\circ\), 135\(\circ\)
- (c)
110\(\circ\), 125\(\circ\)
- (d)
105\(\circ\), 130\(\circ\)
If each interior angle of a regular octagon is 135°, then the exterior angle of octagon is
- (a)
65°
- (b)
75°
- (c)
45°
- (d)
none of these
The sum of all exterior angles of a convex polygon of n sides is
- (a)
4 right angles
- (b)
\(\frac2 n\)right angles
- (c)
(2n-4) right angles
- (d)
\(\frac n 2\)right angles
ABCD is a rhombus. If \(\lfloor ACB\)=46\(\circ\) , then \(\lfloor ADB\) is equal to
- (a)
34\(\circ\)
- (b)
32\(\circ\)
- (c)
124\(\circ\)
- (d)
44\(\circ\)
In a parallelogram ABCD, the bisectors of \(\lfloor A\) and \(\lfloor B\) meet at O. Then 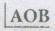 is equal to
is equal to
- (a)
85\(\circ\)
- (b)
90\(\circ\)
- (c)
110\(\circ\)
- (d)
none of these
The area of the greatest circle, which can be inscribed in a square whose perimeter is 120 cm is
- (a)
\(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \times { (15) }^{ 2 }cm^{ 2 }\)
- (b)
\(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \times { (\frac7 2) }^{ 2 }cm^{ 2 }\)
- (c)
\(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \times { (\frac{15} 2) }^{ 2 }cm^{ 2 }\)
- (d)
\(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \times { (\frac9 2) }^{ 2 }cm^{ 2 }\)
The area of a field in the shape of a trapezium measures 1440 m, The perpendicular distance between its parallel sides is 24 m, If the ratio of the parallel sides is 5:3, the length of the longer parallel side is
- (a)
75m
- (b)
45m
- (c)
120m
- (d)
60m
If ABCD is a rectangle of length and width 8 cm, 6 cm respectively, how much is the radius of the circle inscribed in \(\Delta\)BDC?

- (a)
2 cm
- (b)
3 cm
- (c)
4 cm
- (d)
none of these
In a quadrilateral PQRS, the sides and diagonals are related as
- (a)
PQ+QR+RS+SP<PR+QS
- (b)
PQ+QR+RS+SP>2(PR+QS)
- (c)
PQ+QR+RS+SP=2(PR+QS)
- (d)
PQ+QR+RS+SP>(PR+QS)
The difference between the interior and exterior angles of a regular polygon is 60o. The number of sides in the polygon is
- (a)
1
- (b)
6
- (c)
5
- (d)
8







