

SAT Physics - Light
Exam Duration: 45 Mins Total Questions : 30
The figure shows two rays A and B being reflected by a mirror and going as A' and B'. The mirror
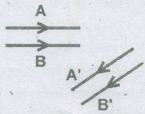
- (a)
is plane
- (b)
is convex
- (c)
is concave
- (d)
may be any spherical mirror
Critical angle for glass water interface is __ (Given aμg =3/2;aμw = 4/3)
- (a)
sin-1(8/9)
- (b)
sin-1(9/8)
- (c)
sin-1(3/4)
- (d)
sin-1(2/3)
A cylindrical lens is required to correct
- (a)
Presbyopia
- (b)
Myopia
- (c)
Astigmatism
- (d)
Hypermetropia
Hypermetropia is due to the _____ of the eye
- (a)
low diverging power
- (b)
low converging power
- (c)
high converging power
- (d)
high diverging power
The latest displacement of a ray of light passing through a glass slab depends on
- (a)
the distance between its opposite faces
- (b)
the angle of incidence
- (c)
both distance between its opposite faces and angle of incidence
- (d)
independent of a distance between the faces and angle of incidence
The decomposition of a beam of white light into its constituent colours is known as
- (a)
scattering
- (b)
dissemination
- (c)
dispersion
- (d)
angular dispersion
Focal length of curved mirror depends on
- (a)
wavelength of light
- (b)
frequency of light
- (c)
material of mirror
- (d)
none
Velocity of light in diamond is:
- (a)
2.1 x 108
- (b)
1.2 x 108
- (c)
1.5 x 108
- (d)
2.5 x 108
According to the sign convention, the distance of object
- (a)
is always positive
- (b)
is always negative
- (c)
may be positive or negative
- (d)
is equal to object height
The part of the lens through which the ray of light passes without suffering deviation is called ______
- (a)
Optical centre
- (b)
Focus
- (c)
Centre of curvature
- (d)
Pole
A convex lens is called _______
- (a)
Converging lens
- (b)
Diverging lens
- (c)
Both converging and diverging lens
- (d)
Refracting lens
A positive magnification greater than unity indicates_______
- (a)
Real image
- (b)
Virtual image
- (c)
Neither real image nor virtual image
- (d)
Distorted image
The image formed by a convex mirror is always ________
- (a)
Real
- (b)
Enlarged
- (c)
Virtual and enlarged
- (d)
Diminished
As you move an object away from a convex mirror, its image becomes _____ and moves towards _______
- (a)
Smaller, infinity
- (b)
Smaller, focus
- (c)
Enlarged, infinity
- (d)
Enlarged, focus
The image formed by a plane mirror is always ________
- (a)
Real and erect
- (b)
Virtual and erect
- (c)
Real and inverted
- (d)
Virtual and inverted
The relation between the focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror is
- (a)
f/2 +1 = f
- (b)
R + 2 = f
- (c)
f=R/2
- (d)
f=2R
Image formed by a concave mirror is erect and enlarged.What is the position of the object?
- (a)
Between focus F and the center of curvature
- (b)
At the center of curvature
- (c)
Beyond the center of curvature
- (d)
Between pole and the focus
Which type of wave cannot travel through a vacuum?
- (a)
infra-red radiation
- (b)
microwaves
- (c)
sound waves
- (d)
X-rays
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed
- (a)
between the pole and the focus of the reflector
- (b)
very near to the focus of the reflector
- (c)
between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector
- (d)
at the centre of curvature of the reflector
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in Figure. Which one of them is correct?
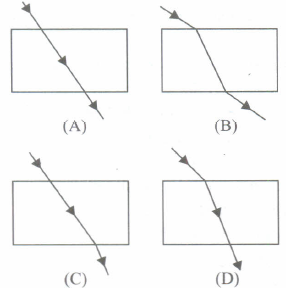
- (a)
A
- (b)
B
- (c)
C
- (d)
D
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in Figure?
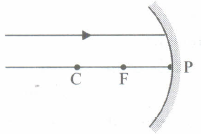
- (a)
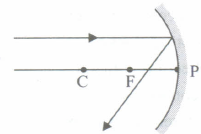
- (b)
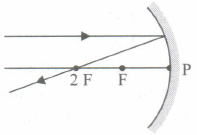
- (c)
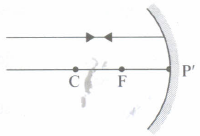
- (d)
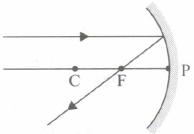
The far point of a myopic eye is 40 cm. The focal length of the lens needed to correct the vision so that distant objects can be seen distinctly is
- (a)
40 cm
- (b)
-40 cm
- (c)
\((\frac{1}{40})\)cm
- (d)
\((\frac{1}{0.4})\)cm
If a ray of light falls normally on a glass slab, then the angle of reflection in glass slab is
- (a)
0°
- (b)
30°
- (c)
45°
- (d)
90°
If ng and nw are absolute refractive indices of glass and water, then the refractive index of glass w.r.t water is
- (a)
ng/nw
- (b)
nw/ng
- (c)
(ng - nw)
- (d)
(ng + nw)
The graph drawn between 1/u along x-axis and 1/v along y-axis for a convex lens is
- (a)
.png)
- (b)
.png)
- (c)
.png)
- (d)
.png)
If V1 and V2 are the velocities of light
in media of refractive indices n2 and
n2 respectively, such that V1 > V2 then
- (a)
n1 < n2
- (b)
n1 > n2
- (c)
n1 = n2
- (d)
\({n_1\over n_2}\le 1\)
A lens of Il = 1.5 produces a virtual image of a real object in air. If the whole set up is immersed in water, the image will
- (a)
Shift closer to lens
- (b)
Shift a way from lens
- (c)
remain in same point
- (d)
depend on whether concave or convex len
If an incident ray is successively reflected by three plane mirror kept mutually perpendicular as shown in the figure, the deviation suffered by the ray is

- (a)
0°
- (b)
90°
- (c)
180°
- (d)
Depends on the angle of incidence
A parallel beam of light consisting of red, green and blue colours is incident on a right angled isosceles glass prism as shown in the figure. Which colour will be separated from the others by the prism?
Given that refractive indices of glass for red, green and blue colours are 1.49, 1.44 and 1.47 respectively.

- (a)
Red only
- (b)
Green only
- (c)
Blue only
- (d)
Both red and blue
An air bubble is inside water. The refractive index of water is 4/3. At what distance from the air bubble should a point object be placed so as to form a real image at the same distance from the bubble
- (a)
2R
- (b)
3R
- (c)
4R
- (d)
the air bubble cannot form a real image







