

SAT Physics - Motion
Exam Duration: 45 Mins Total Questions : 30
If a ball is thrown vertically upwards with speed u, the distance covered during the last t seconds of its, ascent is
- (a)
1/2 gt2
- (b)
ut
- (c)
ut- 1/2 gt2
- (d)
(u + gt)t
A ball is thrown from height h and another from 2 h. The ratio of time taken by the two balls to reach ground is
- (a)
\(\sqrt { 2 } :1\)
- (b)
\(1:\sqrt { 2 } \)
- (c)
2:1
- (d)
1:2
A scooterist covers a distance of 6 km in 5 min. calculate the speed in mls.
- (a)
20 m/s
- (b)
40 m/s
- (c)
15m/s
- (d)
30 m/s
The ratio of SI units to CGS units of velocity is
- (a)
10-2
- (b)
102
- (c)
10
- (d)
10-1
The velocity of a particle increases from u to v in at during which it covers a distance s. If the particle uniform acceleration, which one of the following equations does not apply to the motion?
- (a)
2s=(v+u)t
- (b)
\(a=\frac { v-u }{ t } \)
- (c)
v2=u2-2as
- (d)
s=(u+1/2 at)t
When a graph of one quantity versus another results in a straight line, the quantities are
- (a)
Directly proportional
- (b)
Constant
- (c)
Inversely proportional
- (d)
Independent of each other
What is the SI unit of speed?
- (a)
km/h
- (b)
m/s
- (c)
m/min
- (d)
km/s
Km/h2 is a unit of ______
- (a)
Velocity
- (b)
Speed
- (c)
Acceleration
- (d)
Distance
Motion along a straight line is called ____ motion.
- (a)
Rectilinear motion
- (b)
Circular motion
- (c)
Oscillatory motion
- (d)
Parabolic
A car is moving with a speed of 36 km/h. Its speed in m/s is
- (a)
10
- (b)
100
- (c)
2
- (d)
1
From the given v - t graph, it can be inferred that the object is
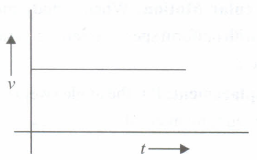
- (a)
in uniform motion
- (b)
at rest
- (c)
in non-uniform motion
- (d)
moving with uniform acceleration
Area under a v - t graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit
- (a)
m2
- (b)
m
- (c)
m2
- (d)
ms-1
Four cars A, B, C and D are moving on a levelled road. Their distance versus time graphs are shown in Fig. Choose the correct statement
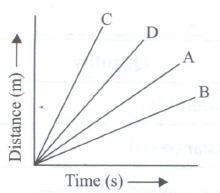
- (a)
Car A is faster than car D.
- (b)
Car B is the slowest.
- (c)
Car D is faster than car C.
- (d)
Car C is the slowest.
A body whose position with respect to surrounding does not change, is said to be in a state of:
- (a)
Rest
- (b)
Motion
- (c)
Vibration
- (d)
Osciliation
Examples of vector quantities are:
- (a)
velocity, length and mass
- (b)
speed, length and mass
- (c)
time, displacement and mass
- (d)
velocity, displacement and force
Time is an example of:
- (a)
Scalar
- (b)
Vector
- (c)
Scalar or vector
- (d)
Neither scalar nor vector
A speed:
- (a)
is always positive
- (b)
is always negative
- (c)
may be positive as well as negative
- (d)
is neither zero nor negative
Mere per second is not the unit of:
- (a)
Speed
- (b)
Velocity
- (c)
Displacement
- (d)
None of them
In figure BC represents a body moving:
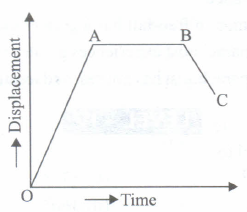
- (a)
Backward with uniform velocity
- (b)
Forward with uniform velocity
- (c)
Backward with non-uniform velocity
- (d)
Forward with non-uniform velocity
Five telegraph poles are positioned at equal distances along the side of a road.
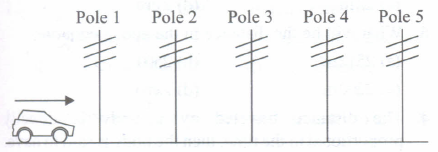
A car accelerates until it is level with pole 4. The car then continues along the road at a steady speed. The times taken to travel between one pole and the next are measured. Which time is the greatest?The time between
- (a)
pole 1 and pole 2.
- (b)
pole 2 and pole 3.
- (c)
pole 3 and pole 4.
- (d)
pole 4 and pole 5.
The following statements are about motion.
1. A plane flies due East for 600 km.
2. A runner's average speed in a race around a track is 5 m/s.
3. A snail crawls at 3 mm/s in a straight line towards a lettuce.
4. A tourist travels 500 km on a journey. Which statements describe vector quantities?
- (a)
1 and 2
- (b)
1 and 3
- (c)
2 and 3
- (d)
2 and 4
In a circular path of radius 1m, a mass of 2kg moves with a constant speed 10 ms-1. The angular speed in radian/sec, is:
- (a)
5
- (b)
10
- (c)
15
- (d)
20
The relationship between average speed, time and distance is
- (a)
Average speed = distance time
- (b)
Average speed =\(\frac{total\quad distance}{total\quad time}\)
- (c)
Time = average speed/distance
- (d)
Distance = average speed time
A particle revolves around a circular path. The acceleration of the particle is
- (a)
along the circumference of the circle
- (b)
along the tangent
- (c)
along the radius
- (d)
zero
Which of the following is not an example of linear motion
- (a)
a book at rest
- (b)
a body in uniform circular motion
- (c)
wheel rotating at uniform speed on road
- (d)
a body roiling down an inclined plane
The velocity of a body increases for some time, then remains constant and then decreases until it comes to rest. When velocity is plotted against time, the figure obtained is
- (a)
straight line
- (b)
circle
- (c)
trapezium
- (d)
square
Area under the velocity-time graph gives
- (a)
the time taken by a moving object
- (b)
the distance travelled by a moving object
- (c)
the acceleration of a moving object
- (d)
none of the above
A particle experiences constant acceleration for 20 s after starting from rest. If it travels a distance S1 in the first 10 second and a distance S2 in the next 10 second, then
- (a)
S2 = 2S1
- (b)
S2=3S1
- (c)
S2=4S1
- (d)
S2=5S1
A body falling under gravity moves with uniform:
- (a)
speed
- (b)
velocity
- (c)
momentum
- (d)
acceleration
A stone is dropped into a lake from a tower 500 m high. The sound of the splash will be heard by a man on the tower after
- (a)
21 s
- (b)
10 s
- (c)
11.5 s
- (d)
14 s







